Understanding Sheet Metal Perforated Panels
Sheet metal perforated panels are versatile and innovative products used in a wide array of applications, ranging from architectural design to industrial manufacturing. Characterized by a pattern of holes, these panels offer not only aesthetic appeal but also functional benefits that have made them increasingly popular in contemporary design and engineering.
Construction and Characteristics
Perforated panels are typically made from various types of sheet metal, including aluminum, steel, and stainless steel. The process of perforation involves creating holes in the sheet metal using methods such as laser cutting, punching, or water jet cutting. The design of the holes can vary significantly, from simple round shapes to complex geometric patterns. This customization allows architects and designers to create unique designs that complement their projects while fulfilling specific performance requirements.
One of the key characteristics of perforated panels is their ability to balance light and sound within a space. The holes in the panels enable natural light to filter through while maintaining a level of privacy. This makes them ideal for use in building facades, skylights, and interior partitions. Additionally, their acoustic properties help reduce noise levels in busy environments, making them suitable for applications in commercial spaces and public buildings.
Applications
The applications of sheet metal perforated panels are extensive. In architecture, they are often used for facades, ceilings, and interior walls, providing a modern look while enhancing functionality. For instance, many contemporary buildings utilize perforated aluminum panels as exterior cladding, which not only protects the structure but also contributes to energy efficiency by regulating temperature and light.
sheet metal perforated panels
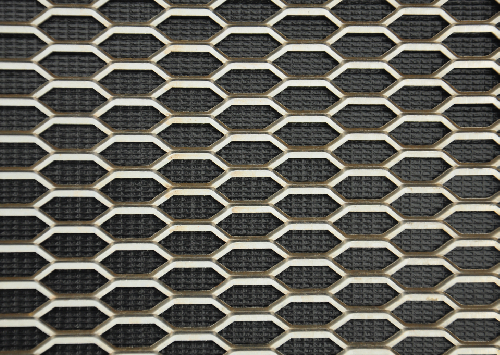
In industrial settings, perforated panels are employed in filtration systems, screens, and safety barriers. Their durable nature and resistance to corrosion make them ideal for harsh environments. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and food processing often rely on perforated panels for equipment and machinery protection, given their strength and reliability.
Moreover, perforated panels are increasingly being used in sustainable building practices. As the demand for eco-friendly materials rises, manufacturers are developing perforated panels from recycled metals, making them both environmentally responsible and economically viable. Their lightweight nature also means reduced transportation costs and energy expenditure, appealing to eco-conscious designers.
Design Flexibility
One of the standout features of sheet metal perforated panels is their design flexibility. The variety of hole patterns, sizes, and arrangements offers architects and designers an almost limitless range of creative options. Whether aiming for a minimalist look or a bold statement, perforated panels can be tailored to meet specific design goals.
Additionally, these panels can be painted or finished in various ways, allowing for complete integration into existing color schemes or design themes. Beyond their utility, they serve as a canvas for artistic expression, adding a distinctive touch to any project.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sheet metal perforated panels play a significant role in modern architecture and industrial design. Their combination of aesthetic versatility, functional properties, and sustainable potential positions them as a favored choice among designers and engineers. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications and designs, further solidifying their place in the future of construction and manufacturing. Whether used in a stylish façade or a practical industrial component, perforated panels embody the perfect blend of form and function.
-
The Best Metal Mesh Solutions: Expanded Aluminum Metal vs. Expanded Stainless Steel Metal
NewsSep.10,2024
-
Round Perforated Sheets vs. Hexagonal Perforated Sheets vs. Embossed Perforated Sheet Metal
NewsSep.10,2024
-
Perforated Metal Sheets
NewsSep.10,2024
-
Experience The Excellence Of Stainless Steel Grating
NewsSep.10,2024
-
Discover the Versatility Of Metal Mesh Expanded Forming Machines
NewsSep.10,2024
-
Discover The Advantages Of Steel Grating For Sale
NewsSep.10,2024
Subscribe now!
Stay up to date with the latest on Fry Steeland industry news.

